In the reaction between MgS and CuCl2, magnesium sulfide (MgS) reacts with copper(II) chloride (CuCl2) to form copper(II) sulfide (CuS) and magnesium chloride (MgCl2). The balanced net ionic equation is
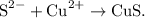
The chemical equation provided is:
![\[ \text{MgS} + \text{CuCl}_2 \rightarrow \text{CuS} + \text{MgCl}_2 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/f0ok3iiiu41qtugksdw9v0pg796mu4lwa3.png)
To write the balanced complete ionic equation, we first need to identify the ions that dissociate in water. Here, MgS and CuCl2 are ionic compounds, so they dissociate into their respective ions:
![\[ \text{Mg}^(2+) + \text{S}^(2-) + \text{Cu}^(2+) + 2\text{Cl}^- \rightarrow \text{CuS} + \text{Mg}^(2+) + 2\text{Cl}^- \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/wbtr2tmipre6cd1cvxe9956o7ipj050v4h.png)
Now, we can cancel out the spectator ions (ions that appear on both sides of the equation):
![\[ \text{S}^(2-) + \text{Cu}^(2+) \rightarrow \text{CuS} + \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/cwh49xvj4xgu2egk97kgg66ilipsz8bu5d.png)
The balanced net ionic equation is:
![\[ \text{S}^(2-) + \text{Cu}^(2+) \rightarrow \text{CuS} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/2w0kjcjgomsgx1ewk2o21uga4b6tjtcurb.png)