Final Answer:
(a) The temperature of the gas is 500 K.*
(b)The new gas temperature after compression is approximately 920 K.
(c) The work done on the gas during the compression is 1646.6 J, and the change in internal energy is 0 J.
(d) The process is isothermal, so there is no change in internal energy.
Step-by-step explanation
(a): We use the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) to find the temperature ((T)). Rearranging the equation, we get (T = PV/nR).
Plugging in the given values, we find
 .
.
(b): For an adiabatic process, we use
 constant. For a monatomic ideal gas,
constant. For a monatomic ideal gas,
 .
.
Using
 , where (V) is the initial volume and \(V'\) is the final volume, we find
, where (V) is the initial volume and \(V'\) is the final volume, we find
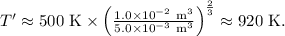
(c): The work done during adiabatic compression is given by
 . The change in internal energy
. The change in internal energy
 is zero for an adiabatic process.
is zero for an adiabatic process.
Plugging in the values, we find
 .
.
(d): Isothermal processes have constant temperature, implying no change in internal energy. This is because
 , and if
, and if
 , then
, then
 .
.