To determine the initial bacteria population, we use the exponential growth formula, plug in the given values, and calculate to find that the initial population was approximately 2,442 bacteria.
Given the bacteria culture had a population of 60,000 after 8 hours with a relative rate of growth of 40%, we need to calculate the initial population. To find the initial population, we can use the formula for exponential growth:
N(t) =
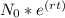
where:
N(t) = the amount of substance after time t
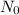 = initial amount of substance
= initial amount of substance
e = the base of the natural logarithm
rt = rate of growth times the time t
Since we know N(t) (60,000), r (40% or 0.4 as a decimal), and t (8 hours), we can rearrange the formula to solve for N0:
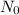 = N(t) /
= N(t) /
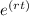
Now, plugging in the values we have:
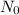 = 60,000 /
= 60,000 /
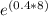
Calculating the exponent first:
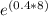 is approximately
is approximately
 , which is about 24.53 when rounded off.
, which is about 24.53 when rounded off.
Therefore,
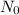 = 60,000 / 24.53
= 60,000 / 24.53
Dividing 60,000 by 24.53 gives us:
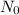 ≈ 2,442
≈ 2,442
Thus, the initial population of the bacteria culture was approximately 2,442 bacteria.