Solution :
Red is dominant over the white leaves and pointed is dominant over smooth.
Red = R , white = r
Pointed = P , smooth = p
Red, pointed x white,smooth ------ Parents
RRPP rrpp
RP rp ----------------- Gametes
RrPp --------
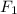
(red, pointed)
When this
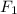 is test crossed,
is test crossed,
RrPp x rrpp ----
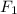 test cross
test cross
Gametes → rp
RP ---------- RrPp - red, pointed - 36 parental type
Rp ---------- Rprp - red, smooth - 14 re- combination
rP ----------- rrPp - white pointed - 10 re- combination
rp ----------- rrpp - white, smooth - 40 - parental type
Total = 100
As this ratio is deviating from 1:1:1:1, it indicated the two genes are linked.
Linkage strength = percentage of crossing over = map distance between the genes.
Percentage crossing = recombination frequency = percentage of recombination.
Recombination frequency
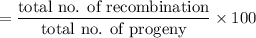
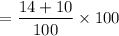
= 24 %
= 24 map units