Answer:
In Java:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a 3 x 3 matrix: ");
double[][] myArr = new double[3][3];
for(int i =0;i<3;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<3;j++){
myArr[i][j] = input.nextDouble();}}
boolean isMarkov = true;
double colsum = 0.00;
for(int i =0;i<3;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<3;j++){
colsum += myArr[j][i];}
if(colsum != 1.00){
isMarkov = false;
break;}
colsum = 0.00;
}
if(isMarkov){ System.out.print("It is a Markov matrix"); }
else{ System.out.print("It is a not Markov matrix"); }
}
}
Step-by-step explanation:
This line prompts the user for a
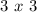 matrix
matrix
System.out.print("Enter a
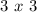 matrix: ");
matrix: ");
This declares a 3 x 3 matrix
double[][] myArr = new double[3][3];
The following iteration gets input for the
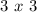 matrix
matrix
for(int i =0;i<3;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<3;j++){
myArr[i][j] = input.nextDouble();}}
This declares and initializes a boolean variable to true
boolean isMarkov = true;
This declares and initializes colsum to 0 i.e. the sum of each column
double colsum = 0.00;
The following iteration sums up each column
for(int i =0;i<3;i++){
for(int j = 0;j<3;j++){
colsum += myArr[j][i];}
This checks if the column sum is not 1
if(colsum != 1.00){
If true that the column sum is not 1, the boolean variable is updated to false
isMarkov = false;
And the loop is terminated
break;}
colsum = 0.00;
}
If isMarkov is true, the system prints that it is a Markov matrix
if(isMarkov){ System.out.print("It is a Markov matrix"); }
If isMarkov is false, the system prints that it is not a Markov matrix
else{ System.out.print("It is a not Markov matrix"); }