Answer:
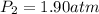
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, according to the ideal gas equation ratio for two states:
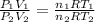
Whereas both n and R are cancelled out as they don't change, we obtain:
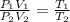
Thus, by solving for the final pressure, we obtain:
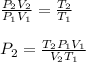
Now, since initial conditions are 1.00 atm, 273.15 K and 17 L and final temperature and volume are 94 + 273 = 367 K and 12 L respectively, the resulting pressure turns out to be:
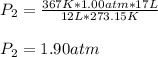
Best regards!