Final answer:
The force on a vertical surface of 350 square feet by a wind with a velocity of 20 miles per hour is approximately 82.8 pounds (Option C).
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the force exerted by the wind on a vertical surface, you can use the formula:
![\[ \text{Force} = (1)/(2) * \text{Air Density} * \text{Wind Velocity}^2 * \text{Drag Coefficient} * \text{Area} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/sr7c7hlxxb3n4fyv3jpb5nz6z8klrgcux3.png)
Given that the wind velocity is (20) miles per hour, the area is (350) square feet, and assuming standard air density and a typical drag coefficient for buildings, we can substitute these values into the formula.
Converting the wind velocity from miles per hour to feet per second
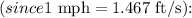
![\[ \text{Wind Velocity} = 20 \, \text{mph} * 1.467 \, \text{ft/s per mph} \approx 29.34 \, \text{ft/s} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/r5gjtjiewormb4ltrg314k078zlakzzurh.png)
Now substitute the values into the formula:
![\[ \text{Force} = (1)/(2) * \text{Air Density} * (29.34 \, \text{ft/s})^2 * \text{Drag Coefficient} * 350 \, \text{ft}^2 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/azd4a1ekd13314gds4og6fbrvpbe3dj9u7.png)
The result is approximately 82.8 pounds. Therefore, the force on the vertical surface is approximately 82.8 pounds, rounded to the nearest tenth of a pound thus option C is correct.