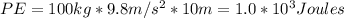The difference between the total work done by the force and the amount of gravitational potential energy gained by the box is due to the conversion of work into other forms of energy. The total amount of gravitational potential energy gained by the box can be calculated using the formula PE = mgh, where m is the mass, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height. In this case, the gravitational potential energy gained by the box is
 Joules.
Joules.
The difference between the total work done by the 80-newton force in pulling the box to the top of the incline and the amount of gravitational potential energy gained by the box is due to the conversion of the work into other forms of energy. When the box is pulled up the incline, some of the work is converted into thermal energy or kinetic energy. Additionally, friction causes an increase in internal energy, so not all the work done becomes gravitational potential energy.
The total amount of gravitational potential energy gained by the box as it is pulled to the top of the incline can be calculated using the formula:
Gravitational potential energy (PE) = mass (m) × acceleration due to gravity (g) × height (h)
Given that the mass of the box is 100 kg, the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s², and the height gained by the box is 10 meters, we can calculate the gravitational potential energy as follows: