Answer:
Final amount = $4279.667.
Explanation:
Formula to get the final amount after 't' years is,
Final amount =
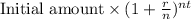
Here 'r' = rate of interest
t = Number of years for the investment
n = Number of compounding in a year
Now we substitute the data given in the question,
Initial amount = $2500
r = 1.8% = 0.018
n = Semi annually = 2
t = 30 years
Final amount =
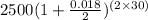
=
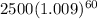
= 4279.667
Therefore, final amount will be $4279.667.