Kepler's third law relates the orbital period T of a celestial body to the semi-major axis a of its orbit. The modified form of Kepler's third law can be expressed as
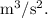 , where k is a constant.
, where k is a constant.
To match the variables and constants with their units:
1. T: Orbital period, measured in seconds (s).
2. a: Semi-major axis, measured in meters (m).
3. k: Constant, unit depends on the units chosen for T and a. If T is in seconds and a is in meters, k will have units of
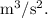
Therefore:
- \(T\) is in seconds (s),
- \(a\) is in meters (m),
- k is in
 (or adjusted based on the chosen units for T and a.
(or adjusted based on the chosen units for T and a.