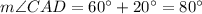The value of x is
 , and the measure of
, and the measure of
 is
is
 .
.
Part A
To write and solve an equation for x using the angle addition postulate, we can start by considering the angles A and C in triangle ABC. These angles are adjacent angles, which means that they share a common vertex and side, but they do not overlap. The angle addition postulate states that the measure of an angle formed by two adjacent angles is equal to the sum of the measures of the two angles.
Therefore, we can write the following equation:
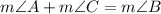
We are given that
 . We are also given that
. We are also given that
 and
and
 . Substituting these values into the equation above, we get:
. Substituting these values into the equation above, we get:
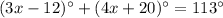
Combining like terms, we get:
7x+8 =
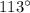
Subtracting 8 from both sides of the equation, we get:
7x =
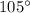
Dividing both sides of the equation by 7, we get:
x =
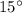
Part B
To find
 , we can substitute
, we can substitute
 into the expression for
into the expression for
 . Therefore,
. Therefore,
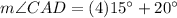
Simplifying the expression, we get: