Based on the observed changes, the metabolic process likely occurring in the organelle is the Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs cycle) as evidenced by decreased Acetyl CoA, increased
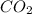 ,
,
 , and decreased FAD. Here option D is correct.
, and decreased FAD. Here option D is correct.
Based on the changes observed in the molecules after incubating the newly discovered organelle, it appears that the metabolic process most likely taking place is the Citric Acid Cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle). Here's a breakdown of the changes and their association with the citric acid cycle:
Glucose: No change - The citric acid cycle typically does not directly consume glucose.
Pyruvate: No change - Pyruvate is usually converted to acetyl CoA before entering the citric acid cycle.
Acetyl CoA: Decrease - Acetyl CoA is consumed in the citric acid cycle to produce energy-rich molecules.
 : No change - The citric acid cycle itself does not directly consume oxygen.
: No change - The citric acid cycle itself does not directly consume oxygen.
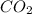 : Increase - The citric acid cycle involves the decarboxylation of molecules, leading to the release of carbon dioxide.
: Increase - The citric acid cycle involves the decarboxylation of molecules, leading to the release of carbon dioxide.
 : Increase -
: Increase -
 is produced as a result of the citric acid cycle.
is produced as a result of the citric acid cycle.
FAD: Decrease - FAD is likely being reduced to
 during the cycle.
during the cycle.
Therefore, based on these changes, the metabolic process most likely occurring in the organelle is the Citric Acid Cycle (D).