a. After-tax cost of debt is 6.75%, cost of preferred stock is 11%, cost of retained earnings is 2.4%, and cost of new common stock is 8.24%.
b. Cost of common equity from retained earnings using CAPM is 14.93%.
c. Cost of new common stock based on CAPM is 2.4%.
d. WACC is 8.89%.
a.
![\[ \text{After-tax cost of debt:} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/2507ygqdoxua2xd9wpnx5w6kttxzihqq6h.png)
The cost of debt is given as 9%. Since it is before-tax, the after-tax cost of debt can be calculated as follows:
![\[ \text{After-tax cost of debt} = \text{Cost of debt} * (1 - \text{Tax rate}) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/wgtware1mpnpmhyj22h2vdtej7y6aua4n2.png)
![\[ \text{After-tax cost of debt} = 0.09 * (1 - 0.25) = 0.0675 \text{ or } 6.75\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/and7fj7406hw8fmgarjuogsezo7qutwdqz.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of preferred stock:} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/79bnvs79atui386g1wk335uv0obm6djvwj.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of preferred stock} = \frac{\text{Dividend per share}}{\text{Price per share}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/byox54s3817klb1hbufrbrlnde1bx8aydk.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of preferred stock} = (3.85)/(35.00) \approx 0.11 \text{ or } 11\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/4mb6z9u5ua705qizejkpnbz64v7h5e65cs.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of retained earnings:} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/f50gl2zib1pxd37l998v9u86h3x11uzbkx.png)
Since Skye's earnings per share (EPS) last year were $3.75, the cost of retained earnings is the dividend payout ratio times the EPS:
![\[ \text{Dividend Payout Ratio} = \frac{\text{Dividends}}{\text{Earnings per share}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/9lc1npg1ziwcg2f7c8gf5jy33z1cdxcv33.png)
![\[ \text{Dividend Payout Ratio} = (2.85)/(3.75) \approx 0.76 \text{ or } 76\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/b0xsyhy1pfkqoqjv7yqxqcrqvvc9qdz1w4.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of retained earnings} = \text{Retention Ratio} * \text{Return on Equity (ROE)} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/136gj67kekz7i26e1iuh1q54br99o5mq77.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of retained earnings} = 0.24 * 0.10 \approx 0.024 \text{ or } 2.4\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/bpdrehf8s9ci0u1yayqpw0byrh7ubiq9pp.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of new common stock:} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/zs5do02rhqobv02vje44w3pdt5yp4ogsse.png)
The cost of new common stock is calculated using the DCF method, considering the flotation cost:
![\[ \text{Cost of new common stock} = \frac{\text{Dividends per share}}{\text{Net issuing price}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/t1s03ynsqvsuz71raw0bxh8ppnscq1wupo.png)
![\[ \text{Flotation cost} = 0.09 * 50.00 = 4.50 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/ykp9xgyl2g1jfvqe4sondt1pdim8chm5zh.png)
![\[ \text{Net issuing price} = 50.00 - 4.50 = 45.50 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/7cp34l1dxgzzfwsgqymge9ht6xyw6o8608.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of new common stock} = (3.75)/(45.50) \approx 0.0824 \text{ or } 8.24\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/qo5z54i6pf28760qk8qkv9cldsm5km342v.png)
b.
![\[ \text{Cost of common equity from retained earnings using the CAPM method:} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/5vxmgkdpznsoym90z4c9605xzskvah21kg.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of common equity from retained earnings (re)} = \text{Risk-free rate} + (\text{Beta} * \text{Market risk premium}) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/ybhinhc3nnuhvhc9slfvhbyjcrx6e1wtyw.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of common equity from retained earnings (re)} = 0.06 + (1.786 * 0.05) = 0.1493 \text{ or } 14.93\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/6h2jxsdmji5f9f7i43m2wqiyk57gx8mk6r.png)
c.
![\[ \text{Cost of new common stock based on the CAPM:} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/us8o8123y8a3ikx9icy8d58qsjmrttxf8a.png)
Using the CAPM, the cost of new common stock is given by:
![\[ \text{Cost of new common stock (rs)} = \text{Risk-free rate} + (\text{Beta} * \text{Market risk premium}) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/e5x6svnlbmyrolymxeps9iv65pgk1030e3.png)
![\[ \text{Cost of new common stock (rs)} = 0.06 + (1.786 * 0.05) = 0.1493 \text{ or } 14.93\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/v8pus2akog44lea8xbjagqt0h6tv92uv3b.png)
The difference between the cost of retained earnings (
 ) and the cost of new common stock (
) and the cost of new common stock (
 ) is:
) is:
![\[ \text{Difference} = r_e - r_s \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/dir1mdb5f1sl3yj9r58udnyvaeu8bvpfiw.png)
![\[ \text{Difference} = 0.024 - 0.1493 = -0.1253 \text{ or } -12.53\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/76t9jyjl9hkd1pyodnliv8j6sap0t1s94h.png)
The cost of new common stock based on the CAPM is
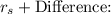
![\[ \text{Cost of new common stock based on the CAPM} = 0.1493 - 0.1253 = 0.024 \text{ or } 2.4\% \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/urxdttu2na81rpywkzx8vj48zcsy1z9zzk.png)
d.
![\[ \text{Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC):} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/d4albf5rmfymckpze2eipn8knikqxn66l8.png)
![\[\text{WACC} = \text{Weight of debt} * \text{Cost of debt} * (1 - \text{Tax rate}) + \text{Weight of preferred stock} * \text{Cost of preferred stock} + \text{Weight of common equity} * \text{Cost of common equity}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/pki15bisayb9bngmid5q6irbrvlgfaeao5.png)
![\[ \text{Weight of debt} = \frac{\text{Total debt}}{\text{Total liabilities and equity}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/e1n72hgiwenk32b9s3p391ioh2qydffkgy.png)
![\[ \text{Weight of debt} = (0.825)/(4.000) = 0.20625 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/x0nv9i20shtsl4kj4n09wssqt6p6o5hjq6.png)
![\[ \text{Weight of preferred stock} = \frac{\text{Market value of preferred stock}}{\text{Total liabilities and equity}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/vdfjpvmb51lvvavecm2aop06cksuvtwzmd.png)
![\[ \text{Weight of preferred stock} = (15,000 * 35.00)/(4,000) = 0.328125 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/ymqyv4yb8cgpx35v7m9ueazaprd3rmtax7.png)
![\[ \text{Weight of common equity} = \frac{\text{Market value of common equity}}{\text{Total liabilities and equity}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/z36z5sw7lgf3gmlljtj2xfvp9uyjpkax9j.png)
![\[ \text{Weight of common equity} = ((40,000 * 50.00) + 975)/(4,000) = 0.465625 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/sb23qyzhyfelngk3n30nfg6xetopa49e2i.png)
![\[\text{WACC} = (0.20625 * 0.0675) + (0.328125 * 0.11) + (0.465625 * 0.024)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/ubb5uybt9isucso6p5zn9fe8e568nix8g7.png)
![\[ \text{WACC} \approx 0.0417 + 0.03605 + 0.01115 \approx 0.0889 \text{ or } 8.89\%\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/t2pcqlg4kqqxb7rgsv4pj4ob605gb5eu2x.png)
So, the WACC assuming only retained earnings for equity is 8.89%, and the WACC if new common stock is issued is also 8.89% (using the simple average).