Answer:
θ = 63.5º
Step-by-step explanation:
- When a ray of light strikes the separation surface between two transparent media with different index of refraction, part of the light remains in the first medium, and part transmits to the second one , according to the Snell's Law, as follows:
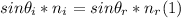
where θi = angle of incidence (with the normal to the surface)
θr = angle of refraction (with the normal to the surface)
ni = index of refraction of denser medium = 1.520
nr = index of refraction of less dense medium = 1.361
- When the angle of refraction is equal to a right angle, this means that the light is parallel to the surface, and remains within the first medium completely.
- The angle of incidence for this particular angle, is called the limit angle, and is the principle of operation of fiber optics, which are composed by a strand of glass, surrounded with another material, which index of refraction is lower than the fiber's, preventing light to go outside the fiber.
- In our case, replacing ni, nr, and θr = 90º in (1), we get:
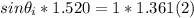
- Solving for sin θ₁ :
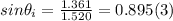
⇒ θi = sin⁻¹ (0.895) = 63.5º