Complete question:
Consider the hypothetical reaction 4A + 2B → C + 3D
Over an interval of 4.0 s the average rate of change of the concentration of B was measured to be -0.0760 M/s. What is the final concentration of A at the end of this same interval if its concentration was initially 1.600 M?
Answer:
the final concentration of A is 0.992 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
time of reaction, t = 4.0 s
rate of change of the concentration of B = -0.0760 M/s
initial concentration of A = 1.600 M
⇒Determine the rate of change of the concentration of A.
From the given reaction: 4A + 2B → C + 3D
2 moles of B ---------------> 4 moles of A
-0.0760 M/s of B -----------> x
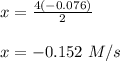
⇒Determine the change in concentration of A after 4s;
ΔA = -0.152 M/s x 4s
ΔA = -0.608 M
⇒ Determine the final concentration of A after 4s
A = A₀ + ΔA
A = 1.6 M + (-0.608 M)
A = 1.6 M - 0.608 M
A = 0.992 M
Therefore, the final concentration of A is 0.992 M.