Answer:
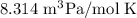
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us find the unit of the gas constant R from the ideal gas equation. We substitute the units of the quantities rearrange them and get the units of the gas constant.
P = Pressure = Pa
V = Volume =
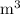
n = Moles = mol
T = Temperature = K
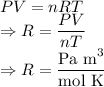
Here,
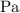 is used so the gas constant value that must be used is
is used so the gas constant value that must be used is
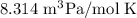 .
.