This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
An owner of a home in the Midwest installed solar panels to reduce heating costs. After installing the solar panels, he measured the amount of natural gas used y (in cubic feet) to heat the home and outside temperature x (in degree-days, where a day's degree-days are the number of degrees its average temperature falls below 65oF) over a 23-month period.
He then computed the least-squares regression line for predicting y from x and found it to be: y^=80+16x.
How much, on average, does gas used increase for each additional degree-day?
Answer : ______ cubic feet.
(Give your answer as a whole number.)
Answer:
Amount of natural gas used increased by 19 cubic feet.
Explanation:
Given the data in the question;
Let the dependent variable y be the amount of natural gas used ( ft³ )
Also let an independent variable x be be the degree days temperature ( in °F)
So the least squares regression equation is;
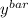 = 80 + 16x
= 80 + 16x
or
amount_of_natural_gas_used = 80 + 16(degree_days_temperature
Th slope or the standardized regression coefficient of the given regression equation is;
b₁ = 16
the slope coefficient b₁ = 16 is tells us that for each additional one-degree days temperature, an amount of natural gas used increased by 19 cubic feet.
Therefore, amount of natural gas used increased by 19 cubic feet.