The maximum amount of Fe that could be extracted from 120 grams of
 is approximately 56 grams. Option B is the right choice.
is approximately 56 grams. Option B is the right choice.
The given information describes a two-step process for extracting Fe (s) from
 (pyrite). However, the specific steps are missing from the prompt.
(pyrite). However, the specific steps are missing from the prompt.
To determine the maximum amount of Fe obtainable from 120 grams of
 , we need the complete equation for the first step.
, we need the complete equation for the first step.
Assuming the first step involves roasting
 with oxygen, the balanced equation would be:
with oxygen, the balanced equation would be:
4
 (s) + 11
(s) + 11
 (g) ->
(g) ->
 (s) + 8
(s) + 8
 (g)
(g)
From this equation, we can calculate the theoretical yield of
 obtained from 120 grams of
obtained from 120 grams of
 :
:
Moles of
 = 120 g / 120 g/mol = 1 mol
= 120 g / 120 g/mol = 1 mol
Moles of
 produced = 1 mol
produced = 1 mol
 * (2 mol Fe2O3 / 4 mol
* (2 mol Fe2O3 / 4 mol
 ) = 0.5 mol
) = 0.5 mol
Theoretical yield of
 = 0.5 mol * 160 g/mol = 80 g
= 0.5 mol * 160 g/mol = 80 g
The second step involves reducing
 to Fe using carbon monoxide (CO) as described by the equation:
to Fe using carbon monoxide (CO) as described by the equation:
 (s) + 3 CO(g) -> 2 Fe(s) + 3
(s) + 3 CO(g) -> 2 Fe(s) + 3
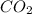 (g)
(g)
Here, we can assume that all the
 produced in step 1 is converted to Fe in step 2. To calculate the theoretical yield of Fe:
produced in step 1 is converted to Fe in step 2. To calculate the theoretical yield of Fe:
Moles of Fe produced = 0.5 mol
 * (2 mol Fe / 1 mol
* (2 mol Fe / 1 mol
 ) = 1 mol
) = 1 mol
Theoretical yield of Fe = 1 mol * 56 g/mol = 56 g
Option B is the right choice.