The patient's temperature reaches its maximum value at approximately 11.5 hours after the illness begins, with a maximum temperature of approximately 100.1 degrees Fahrenheit.
The patient's temperature reaches its maximum value when the derivative of the temperature function, T(t), is equal to zero. To find this maximum, we need to differentiate T(t) with respect to t and set it equal to zero.
The derivative of T(t) with respect to t is given by:
T'(t) = -0.048t + 0.552
To find the value of t when T'(t) = 0, we set -0.048t + 0.552 equal to zero and solve for t:
-0.048t + 0.552 = 0
-0.048t = -0.552
t = -0.552 / -0.048
t = 11.5
Therefore, the patient's temperature reaches its maximum value at 11.5 hours after the illness begins.
To find the maximum temperature, we substitute the value of t into the temperature function, T(t):
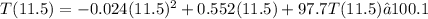
Therefore, the patient's maximum temperature during the illness is approximately 100.1 degrees Fahrenheit.