The pH of the buffer solution is 13.12.
The equilibrium equation for the dissociation of
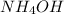 is:
is:
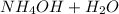 ⇌
⇌
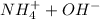
Define the initial concentrations.
The initial concentrations of
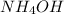 and
and
 are:
are:
![[NH_4OH]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/aydudcj8lbhgo5db3kx05hbkn67je96tra.png) = 0.15 M
= 0.15 M
![[NH_4Cl]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/45te6fedzstyhkiydwor4ipa23t2o4dg8q.png) = 0.25 M
= 0.25 M
Set up an ICE table.
Species Initial concentration (M) Change in concentration (M) Equilibrium concentration (M)
[
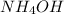 ] 0.15 -x 0.15 - x
] 0.15 -x 0.15 - x
[
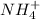 ] 0.25 +x 0.25 + x
] 0.25 +x 0.25 + x
[
 ] 0 +x x
] 0 +x x
Substitute the equilibrium concentrations into the equilibrium equation.
Kb = [
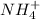 ][
][
 ] / [
] / [
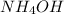 ]
]
1.8 ×
 = (0.25 + x)(x) / (0.15 - x)
= (0.25 + x)(x) / (0.15 - x)
Solve for x.
This equation can be solved for x using the quadratic formula. The value of x is:
x = 7.21 ×
 M
M
Calculate the pOH and pH.
pOH = -log10([OH−])
pOH = -log10(7.21 ×
 )
)
pOH = 2.14
pH = 14 - pOH
pH = 14 - 2.14
pH = 11.86
Question:-
Calculate the pH of the buffer solution containing 0.15 mole of
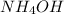 and 0.25 mole of
and 0.25 mole of
 . Kb for
. Kb for
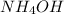 is 1.8 ×
is 1.8 ×
