Answer:
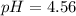
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, given the Henderson-Hasselbach equation, it is possible for us to compute the pH by firstly computing the concentration of the acid and the conjugate base; for this purpose we assume that the volume of the total solution is 0.025 L and the molar mass of the sodium base is 234 - 1 + 23 = 256 g/mol as one H is replaced by the Na:
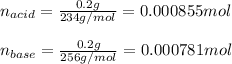
And the concentrations are:
![[acid]=0.000855mol/0.025L=0.0342M](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/ne1l2brwdqykwwhqz39ve88nriu5d0swig.png)
![[base]=0.000781mol/0.025L=0.0312M](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/b1wo9nmj1xaw2iiav9mzkqrs7jz9liwy3k.png)
Then, considering that the Ka of this acid is 2.5x10⁻⁵, we obtain for the pH:
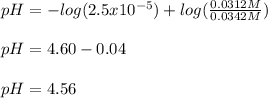
Best regards!