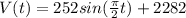Answer:
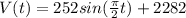
Step-by-step explanation:
The volume of air increases and decreases, hence the volume of air can be represented as a sine function.
A sine function is of the form:
y = Asin(B(x - C)) + D
Where A is the amplitude, B is the frequency, C is the horizontal shift and D is the vertical shift.
Therefore, the total volume of air V(t) in the lungs as a function of time is given by:
V(t) = Asin(B(t - C)) + D
Since the volume of air in and out of the longs is 504 ml, hence the amplitude (A) = 504/2 = 252
There is residual air of 2030 ml minimum in the lungs and a maximum of 2534 ml (2030 ml + 504 ml), hence the vertical shift (D) = (2534 + 2030) / 2 = 2282 ml
The frequency B = 2π / 4 s = π/2
Therefore: