Answer:

Explanation:
The standard form of a linear equation is typically written as
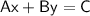 , where
, where
 ,
,
 , and
, and
 are constants, and
are constants, and
 is non-negative.
is non-negative.
To convert the equation
 to standard form, we want to move all terms to one side of the equation and set it equal to zero.
to standard form, we want to move all terms to one side of the equation and set it equal to zero.
Now, to make the coefficient of
 positive, we can multiply the entire equation by -1:
positive, we can multiply the entire equation by -1:

Distribute the negative sign:


Now, the equation in the standard form:
 .
.