At a 0.05 significance level, we do not have enough evidence to reject the claim that the majority of U.S. adults do not believe raising the minimum wage will help the economy.
How to solve
Hypothesis Testing: Minimum Wage and Economy
Null Hypothesis (H ₀): The majority of U.S. adults do not believe raising the minimum wage will help the economy (more than 50% do not believe).
Alternative Hypothesis (H₁): The majority of U.S. adults believe raising the minimum wage will help the economy (more than 50% believe).
Significance Level (α): 0.05
Sample Size (n): 1,000
Sample Proportion (p): 43% (believing)
Test Statistic:
We will use the z-statistic to test this hypothesis. The formula is:
z =
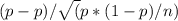
where:
p is the sample proportion (0.43)
p is the population proportion (0.50)
n is the sample size (1,000)
Calculating the z-statistic:
z =

z ≈ -1.40
Decision Rule:
We reject the null hypothesis if the z-statistic falls outside the critical region. At a level of significance of 0.05 and a two-tailed test, the critical region consists of values less than -1.96 or greater than 1.96.
Decision:
Our calculated z-statistic (-1.40) falls within the critical region. Therefore, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion:
At a 0.05 significance level, we do not have enough evidence to reject the claim that the majority of U.S. adults do not believe raising the minimum wage will help the economy.