Answer:
The amount of heat energy that was released by the reaction is 10,460 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
Sensible heat is that which a body or an object receives or releases and causes its temperature to increase or decrease without affecting its molecular structure and therefore its state.
In other words, sensible heat is the amount of heat that a body absorbs or releases without any changes in its physical state (phase change). When a body is supplied or absorbed sensible heat, the temperature varies.
The equation that allows calculating heat exchanges is:
Q = c * m * ΔT
where Q is the heat exchanged by a body of mass m, made up of a specific heat substance c and where ΔT is the temperature variation.
In this case:
- c= 4.184
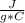
- m= 100 g
- ΔT= Tfinal - Tinitial= 50 C - 25 C= 25 C
Replacing:
Q= 4.184
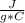 *100 g* 25 C
*100 g* 25 C
Solving:
Q=10,460 J
The amount of heat energy that was released by the reaction is 10,460 J.