a) Input Demand Functions: The demand for labor L is
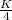 , and the demand for capital K is
, and the demand for capital K is
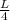 in the production of doors. b) Total Long-Run Cost Function: The total long-run cost is given by C = 10L + 50K, considering labor costing $10 per unit and 8 units of capital priced at $50 each. c) MC, ATC, and AVC: These can be calculated using the relevant derivatives and the given cost functions. d) Lowest Price to Produce: The lowest price is where Marginal Cost (MC) equals the minimum Average Total Cost (ATC). e) Breakeven and Shutdown: At breakeven, door revenue equals total cost; shutdown occurs if total revenue is less than total variable cost.
in the production of doors. b) Total Long-Run Cost Function: The total long-run cost is given by C = 10L + 50K, considering labor costing $10 per unit and 8 units of capital priced at $50 each. c) MC, ATC, and AVC: These can be calculated using the relevant derivatives and the given cost functions. d) Lowest Price to Produce: The lowest price is where Marginal Cost (MC) equals the minimum Average Total Cost (ATC). e) Breakeven and Shutdown: At breakeven, door revenue equals total cost; shutdown occurs if total revenue is less than total variable cost.
a) Production Function and Input Demand Function:
The production function is given by D = f(K, L), where D is the quantity of doors, K is the amount of capital, and L is the amount of labor.
Given that Christine has 4 units of labor (L) and 1 unit of capital (K) to produce 1 door (D), the production function is
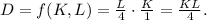
The input demand functions are obtained by partial differentiation:
- For labor (L):
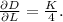
- For capital (K):
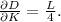
b) Total Long Run Cost Function:
The total long-run cost function is given by C = wL + rK, where w is the price of labor, L is the amount of labor, r is the price of capital, and K is the amount of capital.
c) Marginal Cost (MC), Average Total Cost (ATC), and Average Variable Cost (AVC):
- Marginal Cost (MC) is the derivative of the total cost function with respect to quantity (D).
- Average Total Cost (ATC) is the total cost divided by the quantity (D).
- Average Variable Cost (AVC) is the variable cost divided by the quantity (D).
d) Lowest Price to Produce in the Long Run:
The lowest price to produce in the long run is where MC equals the minimum ATC.
e) Breakeven and Shutdown in the Short Run:
- Breakeven occurs when total revenue equals total cost.
- Shutdown occurs when total revenue is less than total variable cost.
- Each unit of labor (L) costs $10.
- Christine has bought 8 units of capital (K) priced at $50 each.
Breakeven:
Breakeven occurs when total revenue (TR) equals total cost (TC).
TR = D · P
TC = wL + rK
Since TR = TC at breakeven, we can equate the expressions:
D · P = wL + rK
Shutdown:
Shutdown occurs when total revenue (TR) is less than total variable cost (TVC).
TVC = wL
If TR < TVC, then Christine should consider shutting down.