Answer:
Resistance 2.
Step-by-step explanation:
Ohm's law states that at constant temperature, the current flowing in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance in the electrical circuit.
Mathematically, Ohm's law is given by the formula;
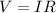
Where;
- V represents voltage measured in voltage.
- I represents current measured in amperes.
- R represents resistance measured in ohms.
Note: Voltage is the same as potential difference.
Given the following data;
Resistance 1 = 10 Ohms
Current 1 = 3 Amperes
Potential difference 1 = current * resistance
Potential difference 1 = 3 * 10
Potential difference 1 = 30 V
To find the potential difference in 2;
Resistance 2 = 5 Ohms
Current 2 = 10 Amperes
Potential difference 2 = 10 * 5
Potential difference 2 = 50 V
Therefore, Resistance 2 has greater potential difference.