To determine the theoretical yield of the reaction we must calculate the moles of reactants that we have. The moles of reactants can be found using the molar mass.
Molar Mass Mg= 24.305g/mol
Molar mass O2=31.998g/mol
Molar mass MgO=40.3044g/mol
Now, the moles of the reactants will be:
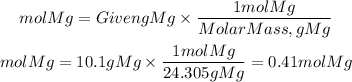
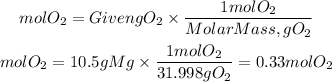
Now, the calculation of theoretical yield will be with the limiting reactant.
Since by stoichiometry we have that the Mg to O2 ratio is 2/1=2 and the current ratio is 0.41/0.33=1.2. Because the current ratio is less than the theoretical one. In this case, the limiting reactant is Mg.
Now, the moles of MgO that we can obtain using the moles of Mg available will be:
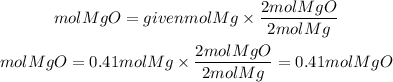
The theoretical yield of MgO (Mass of MgO) will be:
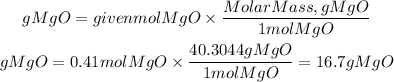
Answer PART B : 16.7 g
Part C
Now, the percent yield will be calculated with the following equation:
![\begin{gathered} PercentYield=(ActualYield)/(TheoreticalYield)*100\% \\ PercentY\imaginaryI eld=(13.3g)/(16.7)*100\operatorname{\%}=79.6\% \end{gathered}]()
Answer PART C: 79.6%