Final Answer:
(a) The acceleration of the system is
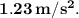
(b) The force exerted by each crate on the other is
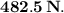
(c) When the crates are reversed, the acceleration remains the same at
 and the force exerted by each crate on the other is
and the force exerted by each crate on the other is
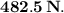
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the acceleration
 , we can use Newton's second law:
, we can use Newton's second law:
![\[ \Sigma F = m \cdot a \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/96fkdkt4fbim9c75ykfm2swy7jbobvfpkq.png)
The net force acting on the system
 is the applied force minus the force of friction. The force of friction
is the applied force minus the force of friction. The force of friction
 can be calculated using the coefficient of kinetic friction
can be calculated using the coefficient of kinetic friction
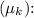
![\[ f_k = \mu_k \cdot N \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/physics/high-school/jem7ztv13o3er1nquujs8g8qqkx1rqspp2.png)
where \(N\) is the normal force. The normal force is equal to the weight of the crates
 since the system is on a horizontal surface.
since the system is on a horizontal surface.
Once we find
 we subtract it from the applied force to get the net force. Finally, we use Newton's second law to find the acceleration.
we subtract it from the applied force to get the net force. Finally, we use Newton's second law to find the acceleration.
For part (b), the force each crate exerts on the other is equal to the force of friction
 because the system is at rest.
because the system is at rest.
For part (c), reversing the crates doesn't change the physics involved. The normal force, friction force, and net force remain the same, resulting in the same acceleration and force between the crates.