1) Write the chemical equation.
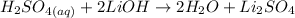
2) List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: H2SO4
Volume: 33.98 mL.
Concentration: unknown
Titrant: LiOH
Volume: 18.19 mL = 0.01819
Concentration: 1.35 M
3) Find moles of LiOH
3.1- Set the equation
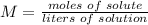
3.2- Plug in the values
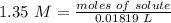
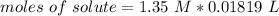
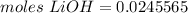
The number of moles of LiOH in the reaction is 0.0246.
4) Find moles of H2SO4
The molar ratio between H2SO4 and LiOH is 1 mol H2SO4: 2 mol LiOH.
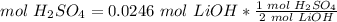
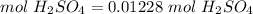
5) Molarity of H2SO4
Sample: H2SO4
Moles: 0.01228
Volume: 33.98 mL.
5.1- Convert mL to L.
1 L = 1000 mL
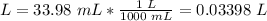
5.2- Set the equation to find molarity.
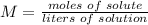
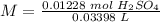
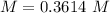
The molarity of the sample is 0.3614 M H2SO4.