Always before starting any calculation it is important to verify that the reaction is balanced. To do this we count the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the reaction. When counting them we have to:
Carbon (C) - 1 atoms
Hydrogen (H) - 4 atoms
Oxygen (O) - 1 atoms
The reaction is balanced, now we proceed to see the stoichiometry of the reaction. We see that for two moles of O2 that react, 1 mole of CO2 is formed, that is, the ratio is 2 to 1.
We must calculate the moles of O2 that correspond to 370.2 grams, for this we use the molar mass of O2 (31.998g/mol).
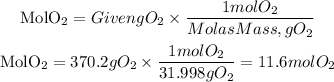
Now, the moles of CO2 produced theoretically will be:
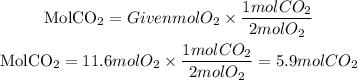
The grams corresponding to the 5.8 moles of CO2 produced will be the theoretical yield of the reaction, and we find it using the molar mass of CO2 equal to 44.01g/mol:
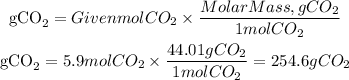
The grams of CO2 found to correspond to the theoretical yield, now the percent yield is found with the following equation:
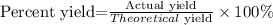
Actual yield=85.9g of CO2
Theoretical yield=254.6g of CO2
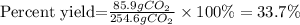
The percent yield of the reaction is 33.7%