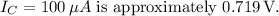Final answer:
The base-emitter voltage corresponding to a collector current of
 is approximately
is approximately
 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
The relationship between the collector current
 and the base-emitter voltage
and the base-emitter voltage
 in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) can be described by the Shockley diode equation:
in a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) can be described by the Shockley diode equation:
where:
 is the collector current,
is the collector current,
 is the saturation current,
is the saturation current,
 is the base-emitter voltage,
is the base-emitter voltage,
 is the thermal voltage, approximately
is the thermal voltage, approximately
 at room temperature.
at room temperature.
Given
 and
and
 , we can rearrange the equation to solve for
, we can rearrange the equation to solve for
 :
:
Solving this equation will give us the base-emitter voltage corresponding to a collector current of
 .
.
Additionally, for the approximate base-emitter voltage for collector currents of
 we can use the fact that the term
we can use the fact that the term
 dominates the equation for typical transistor behavior:
dominates the equation for typical transistor behavior:
Now, let's proceed with solving the first part of the question to find the base-emitter voltage corresponding to
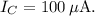
To find the base-emitter voltage corresponding to a collector current of
 we can use the Shockley diode equation:
we can use the Shockley diode equation:
Let's solve this equation for
 :
:
Now, we can calculate the approximate value for
 .
.
Let's calculate this:
So, the base-emitter voltage corresponding to a collector current of