The values are:
![\[ \sin(2x) = -120 \]\\ \cos(2x) = -119 \]\\ \tan(2x) = (120)/(119) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/5y0ph85oftgudh0i6jkz1oryqogh4o7izt.png)
Given that
 and x terminates in quadrant II, you can use trigonometric identities to find
and x terminates in quadrant II, you can use trigonometric identities to find
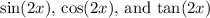
1. Find
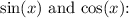
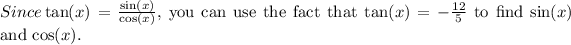
![\[ \tan(x) = (\sin(x))/(\cos(x)) = -(12)/(5) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/suum2xh8gpwifcqbrtr2djwexp9zyljz2g.png)
From this, you can deduce that
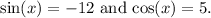
2. Use double-angle formulas:
The double-angle formulas are:
![\[ \sin(2x) = 2\sin(x)\cos(x) \]\\ \cos(2x) = \cos^2(x) - \sin^2(x) \]\\ \tan(2x) = (\sin(2x))/(\cos(2x)) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/hnofjkqw6ufelpxv70deqdnshqh0qvcopg.png)
3. Calculate
 :
:
![\[ \sin(2x) = 2 \cdot (-12) \cdot 5 = -120 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/mqtswvf6t596ly7k4xy1ad0lfljs750jop.png)
4. Calculate
 :
:
![\[ \cos(2x) = 5^2 - (-12)^2 = 25 - 144 = -119 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/2mlnr1b4p3lyk4nc20j5r4yebtp6gykthw.png)
5. Calculate
 :
:
![\[ \tan(2x) = (-120)/(-119) = (120)/(119) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/3i57va2zxtkvtc79q4a2trom6mci4tia93.png)
So, the values are:
![\[ \sin(2x) = -120 \]\\ \cos(2x) = -119 \]\\ \tan(2x) = (120)/(119) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/5y0ph85oftgudh0i6jkz1oryqogh4o7izt.png)