Answer:
The new temperature will be 204.4 K
Step-by-step explanation:
As the volume increases, the particles (atoms or molecules) of the gas take longer to reach the walls of the container and therefore collide with them less times per unit of time. This means that the pressure will be lower because it represents the frequency of collisions of the gas against the walls. In this way pressure and volume are related, determining Boyle's law which says:
"The volume occupied by a certain gaseous mass at constant temperature is inversely proportional to pressure"
Boyle's law is expressed mathematically as:
Pressure * Volume = constant
or P * V = k
Charles's Law consists of the relationship between the volume and the temperature of a certain quantity of ideal gas, which is kept at a constant pressure, by means of a constant of proportionality that is applied directly. For a given sum of gas at a constant pressure, as the temperature increases, the volume of the gas increases and as the temperature decreases, the volume of the gas decreases because the temperature is directly related to the energy of the movement of the gas molecules. .
In summary, Charles's law is a law that says that when the amount of gas and pressure are kept constant, the ratio between the volume and the temperature will always have the same value:
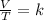
Finally, Gay-Lussac's law can be expressed mathematically as follows:
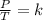
This law indicates that the quotient between pressure and temperature is constant.
This law indicates that, as long as the volume of the container containing the gas is constant, as the temperature increases, the molecules of the gas move faster. Then the number of collisions against the walls increases, that is, the pressure increases. That is, the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to its temperature.
Combined law equation is the combination of three gas laws called Boyle's, Charlie's and Gay-Lusac's law:
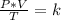
You want to study two different states, an initial state and a final state. It will happen:
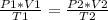
In this case:
- P1= 100 kPa
- V1= 150 mL
- T1= 19 C= 292 K (being 0 C= 273 K)
- P2= 105 kPa
- V2= 100 mL
- T2=?
Replacing:
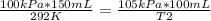
Solving:
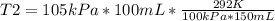
T2= 204.4 K
The new temperature will be 204.4 K