Final answer:
Using Gay-Lussac's Law, the final pressure of the gas when cooled from 177°C to 47°C is calculated by converting temperatures to Kelvin, then using the proportionality of pressure and temperature. The final pressure is determined to be approximately 1.067 atm.
Step-by-step explanation:
To determine the change in pressure of a gas when temperature changes, while volume and amount of gas remain constant, we can use Gay-Lussac's Law, which is part of the gas laws. This law states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (measured in Kelvin), as long as the volume and amount of gas remain constant.
The formula derived from this law is:
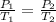
Where:
 is the initial pressure,
is the initial pressure,
 is the initial temperature in Kelvin,
is the initial temperature in Kelvin,
 is the final pressure,
is the final pressure,
 is the final temperature in Kelvin.
is the final temperature in Kelvin.
To solve for
 , we rearrange the formula as follows:
, we rearrange the formula as follows:
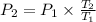
Step 1: Convert temperatures from Celsius to Kelvin by adding 273.15.
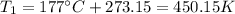
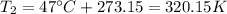
Step 2: Substitute the known values into the rearranged formula and solve for
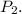
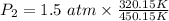
Step 3: Calculate to find the final pressure.
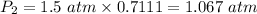
So, the pressure of the gas at 47°C will be approximately 1.067 atm.