This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
Consider an experimental setup with two compartments separated by a phospholipid bilayer membrane containing ion channels selectively permeable only to chloride ions. The left compartment (also called inside) contains 1 mM Cl- and the right compartment (also called outside) contains 100 mM Cl-. What will the electrical potential be when the system attains equilibrium? [ assume body temperature; log 100 = 2, log 10 = 1, log 1 = 0, log 0.1 = -1, log 0.01 = -2]
Options;
a) -62 mV
b) -124 mV
c) +62 mV
d) 0 mV
e) +124 mV
Answer:
the electrical potential be when the system attains equilibrium is –124mV
Option b) –124mV is the correct answer
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the data in the question;
Two compartments are divided by lipid bilayer;
In inside compartment Cl- ion concentration- 1mM and out side of the cell concentration is 100mM
now we apply the Nernst equilibrium potential equation;
Chlorine ion valency is z = –1
So
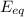 = 62/z × log(ion outside/ ion inside) [for Cl‐ ions]
= 62/z × log(ion outside/ ion inside) [for Cl‐ ions]
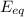 = (62 / –1) x log( 100 / 1 )
= (62 / –1) x log( 100 / 1 )
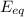 = -62 x 2 =
= -62 x 2 =
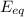 = –124mV
= –124mV
Therefore, the electrical potential be when the system attains equilibrium is –124mV
Option b) –124mV is the correct answer