Answer:
a) The final pressure is 1.68 atm.
b) The work done by the gas is 305.3 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The final pressure of an isothermal expansion is given by:
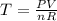
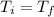
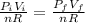
Where:
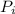 : is the initial pressure = 5.79 atm
: is the initial pressure = 5.79 atm
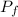 : is the final pressure =?
: is the final pressure =?
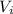 : is the initial volume = 420 cm³
: is the initial volume = 420 cm³
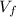 : is the final volume = 1450 cm³
: is the final volume = 1450 cm³
n: is the number of moles of the gas
R: is the gas constant
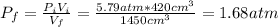
Hence, the final pressure is 1.68 atm.
b) The work done by the isothermal expansion is:
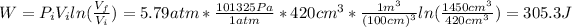
Therefore, the work done by the gas is 305.3 J.
I hope it helps you!