Final Answer:
The standard molar heat of combustion of ethane is -389.5 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
The standard molar heat of combustion of a substance is the enthalpy change for the complete combustion of one mole of the substance under standard conditions (25°C and 1 atm pressure). The combustion of ethane can be represented by the following equation:
 →
→

The standard molar enthalpy change for this reaction is -389.5 kJ/mol. This means that 389.5 kJ of heat are released when one mole of ethane is burned completely under standard conditions.
The standard molar heat of combustion of a substance can be calculated using the following equation:
ΔH°combustion = ΣΔH°f(products) - ΣΔH°f(reactants)
where:
ΔH°combustion is the standard molar heat of combustion (kJ/mol)
ΔH°f is the standard molar heat of formation (kJ/mol)
The standard molar heats of formation of ethane,
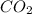 , and
, and
 are -21.1 kJ/mol, -393.5 kJ/mol, and -285.8 kJ/mol, respectively. Plugging these values into the equation, we get:
are -21.1 kJ/mol, -393.5 kJ/mol, and -285.8 kJ/mol, respectively. Plugging these values into the equation, we get:
ΔH°combustion = (2 × -393.5 kJ/mol) + (3 × -285.8 kJ/mol) - (-21.1 kJ/mol) = -389.5 kJ/mol
Therefore, the standard molar heat of combustion of ethane is -389.5 kJ/mol.