Final Answer:
The rate of change in temperature experienced by the fly heading in the direction of the vector h2, −2, 2i is 3√9 units per unit time.
Step-by-step explanation:
The rate of change in temperature for the given vector can be determined by finding the magnitude of the vector, which is the square root of the sum of the squares of its components. In this case, the magnitude is calculated as √(
 + (-2
+ (-2
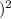 +
+
 ), which simplifies to √(4 + 4 + 4) = √12. To ascertain the rate of change, it’s essential to understand that the vector’s components correspond to the changes along each axis. Therefore, the magnitude of the vector represents the overall change in temperature experienced by the fly.
), which simplifies to √(4 + 4 + 4) = √12. To ascertain the rate of change, it’s essential to understand that the vector’s components correspond to the changes along each axis. Therefore, the magnitude of the vector represents the overall change in temperature experienced by the fly.
Breaking down the vector into its components – h2, −2, 2i – denotes changes along the x, y, and z axes. Considering each component as a single unit change in the respective direction, the resultant magnitude of √12 units implies the overall change in temperature for the fly. This rate is per unit time, signifying the measure of change for each time increment.
This approach ensures an understanding of the rate of change in temperature based on the vector components, enabling the assessment of the overall impact on the fly’s temperature as it moves along the indicated direction. Consequently, a clear calculation of the magnitude offers a concise measure of the rate of change in temperature, essential for anticipating and assessing the fly's experience while moving in the specified direction.