Final answer:
The speed of the runner is found by deriving the distance function and dividing by the derivative of the time function; it is represented by
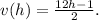
Step-by-step explanation:
The speed of a runner whose distance is represented by the function
 and whose time is represented by
and whose time is represented by
 can be calculated by taking the derivative of the distance function with respect to time, which is the definition of speed in physics. To find the derivative of the distance with respect to time, we must first find the derivative of the distance function with respect to h, and then divide by the derivative of the time function with respect to h.
can be calculated by taking the derivative of the distance function with respect to time, which is the definition of speed in physics. To find the derivative of the distance with respect to time, we must first find the derivative of the distance function with respect to h, and then divide by the derivative of the time function with respect to h.
First, compute the derivative of the distance function,
 Next, compute the derivative of the time function,
Next, compute the derivative of the time function,
 Finally, divide the derivative of the distance function by the derivative of the time function to get the speed,
Finally, divide the derivative of the distance function by the derivative of the time function to get the speed,
 The units of speed would be meters per second, assuming the distance is in meters and time is in seconds.
The units of speed would be meters per second, assuming the distance is in meters and time is in seconds.