Final Answer:
a.
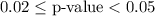
b.
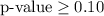
c.
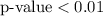
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the p-values for the given hypotheses, a Z-test can be used to compare the sample mean
 to a known population mean
to a known population mean
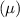 under the null hypothesis
under the null hypothesis
 .
.
The formula to calculate the Z-test statistic is:
![\[ Z = \frac{\overline{x} - \mu}{(s)/(√(n))} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/5ds5xv5ttujoy8kptf0kfduu3uqzgljmmu.png)
a. For
 , and
, and
 :
:
\
![[ Z = (66 - 70)/((12.0)/(√(25))) = (-4)/(2.4) = -1.67 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/x49kntq9ayda1wp2ws54v9av6q1yy107hj.png)
Using a standard normal distribution table or calculator, the corresponding two-tailed p-value is between 0.02 and 0.05.
b. For
 , and
, and
 :
:
![\[ Z = (74 - 70)/((120)/(√(25))) = (4)/(24) = 0.17 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/cw95frsfls9wo9dp0s0ygw61iq1co2of22.png)
The p-value is greater than 0.10, indicating insufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
c. For
 ,
,
 , and
, and
 :
:
![\[ Z = (67 - 70)/((11.3)/(√(25))) = (-3)/((11.3)/(5)) = -1.33 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/1a0j7so1ztpw64eh5mpc14pajl0zdtd4qy.png)
Using a standard normal distribution table or calculator, the corresponding two-tailed p-value is less than 0.01.
Therefore, the p-values for the given sample information fall into the ranges specified in options a, b, and c.