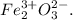Answer:
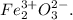
Step-by-step explanation:
Remember that the algebraic sum of the oxidation states of a compound must be zero.
Oxygen always has the oxidation state -2.
In this case, for Fe, we have two options of oxidation state (+2 and +3).
As the algebraic sum must be zero, and we have 3 oxygens in Fe2O3, multiplying -2 by 3, we obtain -6, so we need to find the oxidation state of Fe that sum with -6, the result is zero. If the oxidation state of Fe is +3, multiplying this number by the two Fe that we have, we obtain +6, so the algebraic sum is: -6 +6 = 0.
The ion form, in this case, will look like this: