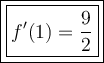Answer:
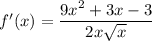
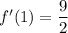
Explanation:
Given rational function:
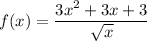
To find f'(x), we can differentiate the function f(x) using the quotient rule:
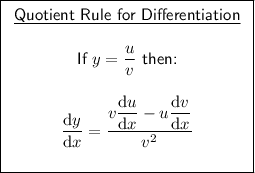
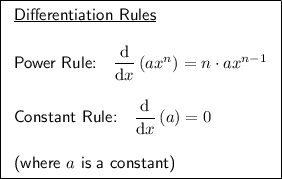
First, identify u and v and differentiate them separately using the power rule and the constant rule:
Therefore:
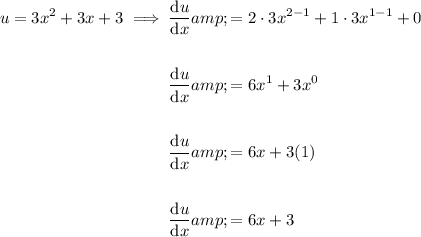
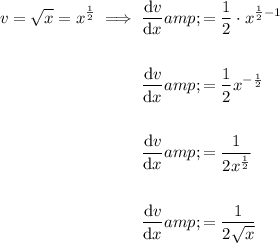
Now, substitute everything into the quotient rule:
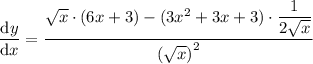
Simplify:
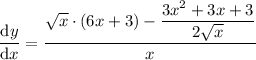
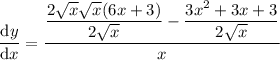
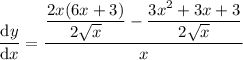
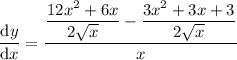
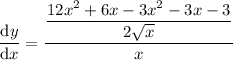
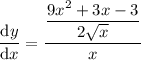
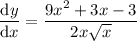
Therefore, the derivative of function f(x) is:
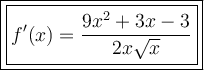
To find f'(1), simply substitute x = 1 into f'(x):
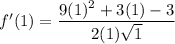
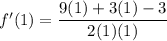
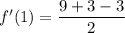
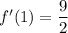
Therefore, the value of f'(1) is: