Answer:
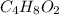
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the combustion of this compound has only one source of carbon, the carbon dioxide, we can compute both mass and moles of carbon in 4.401 grams of CO2:
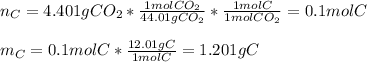
Next, we do the same for hydrogen in water, as the only source of this atom in the products:
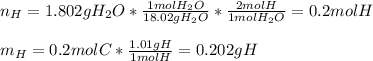
Thus, we compute the mass and then the moles of oxygen considering the 2.203-g sample of dioxane:
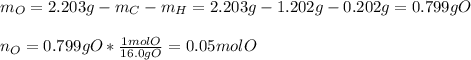
Next, we divide the moles of C, H and O by the moles of O as the fewest in the molecule to find their subscripts in the empirical formula:
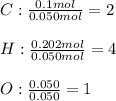
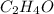
Whose molar mass is 44.1 g/mol. Thus, since the molar mass of the compound is 88.1 g/mol, we see a factor of 2 by which the empirical formula should be multiplied to get the molecular one, therefore, we obtain:
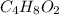
Best regards!