Answer: The partial pressure of oxygen in the tank is 82.95 kPa.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Raoult's law, the partial pressure of a component at a given temperature is equal to the mole fraction of that component multiplied by the total pressure.
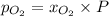
where,
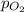 = partial pressure of oxygen
= partial pressure of oxygen
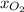 = mole fraction of oxygen
= mole fraction of oxygen
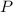 = Total pressure
= Total pressure
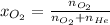 ,
,
where
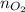 = moles of oxygen =
= moles of oxygen =
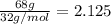
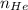 = moles of Helium =
= moles of Helium =
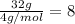
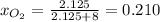
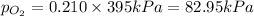
Thus the partial pressure of oxygen in the tank is 82.95 kPa.