Answer: The activation energy, Ea, of the reaction is 89195 Joules
Step-by-step explanation:
The effect of temperature on rate constant is given by Arrhenius equation:
![ln (k_(2))/(k_(1)) = (-E_(a))/(R)[(1)/(T_(2)) - (1)/(T_(1))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/y95oqc16xhfspirxcw3imk40ehtx0adjz2.png)
where
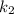 = rate constant at temperature
= rate constant at temperature
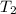
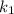 = rate constant at temperature
= rate constant at temperature
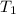
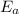 = activation energy
= activation energy
R= gas constant
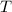 = temperature
= temperature
![ln (17k_1)/(k_(1)) = (-E_(a))/(8.314)[(1)/(300) - (1)/(278)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/b92bnv5yttu4g7v3xx3ie91rmoumrd4ceu.png)
![2.83=(-E_(a))/(8.314)[(1)/(300) - (1)/(278)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/j59n3maqtj9ygxos3ufmbpk6nac8j9dtgk.png)
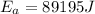
The activation energy, Ea, of the reaction is 89195 Joules