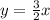A direct linear variation of y with x has the general form:
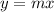
Where m is the ratio of y to x, which is a y divided by x.
Since we know that when x equals 8, y equals 12, we can calculate m, like this:
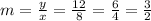
Now that we know that m=3/2, the linear variation equation would be: