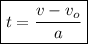Answer:
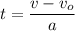
Explanation:
Equations
It's given that the velocity (v) of an object is equal to its initial velocity (vo) plus the product of its acceleration (a) and the elapsed time (t).
The equation that expresses the above relationship is
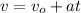
We must write an equation that expresses time in terms of the rest of the variables given above.
Swap the equation:
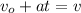
Subtract vo:
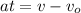
Divide by a: