Answer:
 °
°

Explanation:
T = 20°

t = t minutes
---
When the temperature is increased by
 °
°
 , the time taken for the reaction to occur is 3 minutes faster. So, at the new temperature T +
, the time taken for the reaction to occur is 3 minutes faster. So, at the new temperature T +
 °
°
 , the time is
, the time is
 -
-
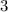 minutes. We can set up a proportion:
minutes. We can set up a proportion:
 =
=

Now, we can solve for
 :
:
 =
=

To get rid of the fractions, you can cross-multiply:
 =
=

 =
=

 =
=

So, the initial time (
 ) is
) is
 minutes.
minutes.
Now to find how much the temperature should be increased for the reaction to occur 5 minutes faster, we can set up a new proportion:
 =
=

Now, solve for Δ
 :
:
 =
=

Cross-multiply:
 Δ
Δ

 Δ
Δ
 =
=

 Δ
Δ
 =
=

 Δ
Δ
 =
=

Now, solve for Δ
 :
:
Δ
 =
=
 =
=

So, the temperature should be increaed by approximately
 °
°
 for the chemical reaction to occur
for the chemical reaction to occur
 minutes faster. However, since temperature increase cannot be negative, this means you need to increase the temperature by
minutes faster. However, since temperature increase cannot be negative, this means you need to increase the temperature by
 °
°
 (approximately) for the reaction to occur 5 minutes faster.
(approximately) for the reaction to occur 5 minutes faster.