The area of trapezium AEDF in its simplest form and in terms of x is

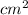 .
.
In Mathematics and Euclidean Geometry, a rectangle refers to a type of quadrilateral in which its opposite sides are equal and all the angles that are formed are right angles.
Based on the definition of a rectangle, we have the following congruent sides in rectangle ABCD;
AD = BC = 5x
AB = DC
AE + 2x = 6x + 2
AE = 6x - 2x + 2
AE = 4x + 2
The area of trapezoid AEDF can be calculated by using this mathematical equation (formula):
Area of trapezoid AEDF, A = 1/2 × (DF + AE) × AD
Area of trapezoid AEDF, A = 1/2 × (2 + 4x + 2) × 5x
Area of trapezoid AEDF, A = 1/2 × (4 + 4x) × 5x
Area of trapezoid AEDF, A = (2 + 2x) × 5x
Area of trapezoid AEDF, A =

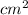
Complete Question:
The diagram shows rectangle ABCD. AEB and DFC are straight lines. All measurements are in cm. The area of trapezium AEDF is A
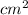 Express the area A in terms of x. Write your answer in its simplest form.
Express the area A in terms of x. Write your answer in its simplest form.